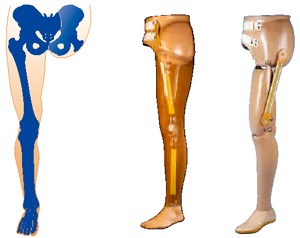
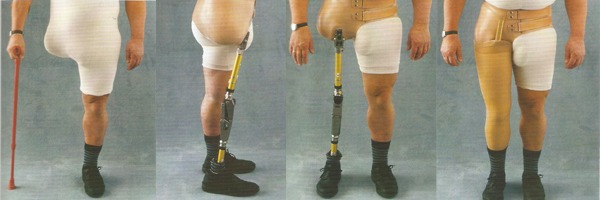
Hip Disarticulation Prostheses
Pelvic prostheses can be fitted with a number of hip amputations, including hemipelvectomy, hip disarticulation, and intertrochanteric amputation. A prosthesis of this kind is necessary if a higher distal amputation level cannot be performed because of an injury or malignancy. Instead of performing a “real disarticulation” in the area of the hip joint, an amputation is performed in the upper section of the femur while the proximal regions of the femur are left intact.
A hemipelvectomy is performed when partial or complete removal of one pelvic half is necessary. In this scenario, the support and enclosure conditions are very difficult. The pelvic socket must be encased in the lower thoracic region because the pelvic sitting area is lost when the ischial tuberosity is removed, and the encasement surface is reduced as a result of the loss of the os ilium. In addition to the motion organs being affected by hemipelvectomies, prosthetic bladder or intestinal outlets are also required, which makes orthopaedic technical fitting much more difficult.